Poster
Surface strain improves molecular adsorption but hampers dissociation for N2 on the Fe/W(110) surface
1Centro de Física de Materiales, CFM/MPC (CSIC-UPV/EHU), Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain
1Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC), Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain
1Dep. de Física de Materiales, UPV/EHU, Donostia-San Sebastián, Spain
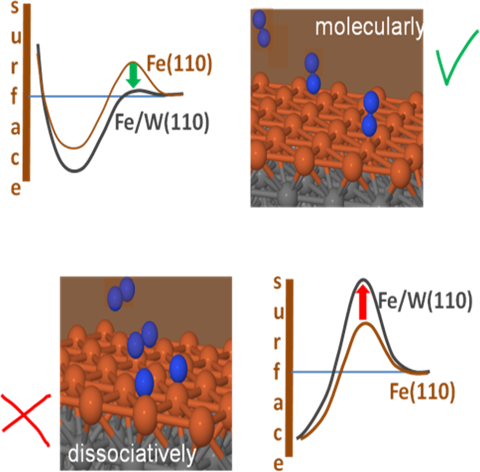
We compare the adsorption dynamics of N2 on the unstrained Fe(110) and on a 10% expanded Fe monolayer grown on W(110) by performing classical molecular dynamics simulations that use potential energy surfaces calculated with density functional theory [1]. Our results allow us to understand the experimental observations of Homann et al. [2] showing that the inertness of Fe(110) towards N2 adsorption disappears on Fe/W(110). In agreement with the reported ARUPS spectra, we also illustrate why N2 adsorbs vertical to the surface though the hollow-parallel adsorption well is energetically more favorable. Surprisingly, we also find that while surface strain favors the molecular adsorption of N2 it seems, on the contrary, to impede the dissociative adsorption. This unexpected observation of a combined molecular adsorption improvement and dissociative adsorption reduction highly contrasts with the common notion that associates surface strain with an overall increase or reduction of all kind of adsorption events. We attribute the present unusual behavior to the excessive stretching of the Fe monolayer that hampers the efficiency of the N–Fe interaction in triggering dissociation. Probably, our finding is not specific of N2 on Fe/W(110) as the central condition of a large tensile stretching can be achieved with many heteroepitaxial surfaces.

Figure 1: Strain favours molecular adsorption, but hampers dissociation for N2 on Fe/W(110).
[1] I. Goikoetxea, J.I. Juaristi, R. Díez Muiño, and M. Alducin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 066103 (2014)
[2] K. Homann, H. Kuhlenbeck, and H.-J. Freund, Surf. Sci. 327, 216 (1995)