Poster
Accounting for van der Waals forces in DFT-based calculations of He and Ne diffraction from metal surfaces
1Departamento de Química, Módulo 13, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Cantoblanco 28049, Madrid, Spain
2Instituto Madrileño de Estudios Avanzados en Nanociencia (IMDEA-Nanociencia), Cantoblanco 28049, Madrid, Spain
Motivated by recent experimental studies about He, Ne and Ar diffraction from a Ru(0001) surface [1], where the last two cases display anticorrugation effects, i.e. corrugation inversion, and by the possibility of using van der Waals (vdW) DFT functionals which allow one to simulate accurately the mentioned experiments, we have studied these systems from a theoretical point of view, aiming to determine the role of vdW interactions on the anticorrugation phenomena observed in the mentioned diffraction processes. To achieve this task, we built the 3D potential energy surfaces (PESs) based on periodic DFT calculations performed by means of the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) [2].
We tested different vdW functionals during these calculations in order to simulate the dispersion forces. Finally, the diffraction spectra are being computed using both classical and quantum dynamics simulations. Although diffraction is a 'pure' quantum phenomenon and quantum dynamics is, in principle, unavoidable to study our system, a classical analysis based on parallel momentum binning [3] has already been revealed as a very useful tool to mimic and analyze diffraction spectra [4,5].

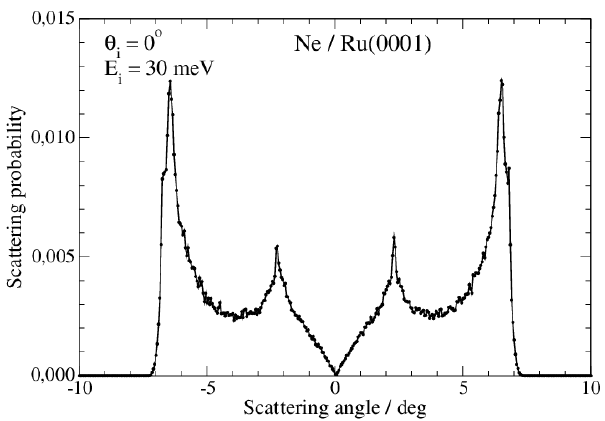
Figure 1: Scattering probability of Ne over Ru(0001) at normal incidence. The scattering distribution presents a classical rainbow, which is proportional to the surface corrugation and will therefore determine the diffraction distribution.
[1] M. Minniti et al, J.Phys. Condens. Matter 24, 354002 (2012)
[2] G. Kresse and J. Hafner, Phys. Rev. B 47, 558 (1993)
[3] C. Ray and J. Bowman, J. Chem. Phys. 63, 5231 (1975)
[4] D. Farías et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 24104 (2004)
[5] C. Díaz et al, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 13671 (2012)